In the rapidly evolving world of automation, the integration of programmable logic controllers (PLCs) into control panel design has become increasingly essential. PLCs serve as the backbone of modern industrial control systems, allowing for greater flexibility, reliability, and efficiency in managing various processes. As engineers and designers strive to create optimal control panels, understanding the intricacies of integrating PLC in control panel design is crucial for meeting the demands of contemporary applications.
The effectiveness of control panels largely depends on how well PLCs are implemented. This involves not only selecting the right hardware but also ensuring that the design maximizes functionality while minimizing risks. By adopting best practices and strategic approaches, designers can create control panels that not only perform reliably but also simplify troubleshooting and maintenance. In the following sections, we will explore the top 10 tips for using PLC in control panel design, offering valuable insights that can help enhance the performance and longevity of your systems. Whether you are a seasoned engineer or just starting in the field, these guidelines will serve as a roadmap for successful PLC integration, ultimately leading to improved project outcomes.
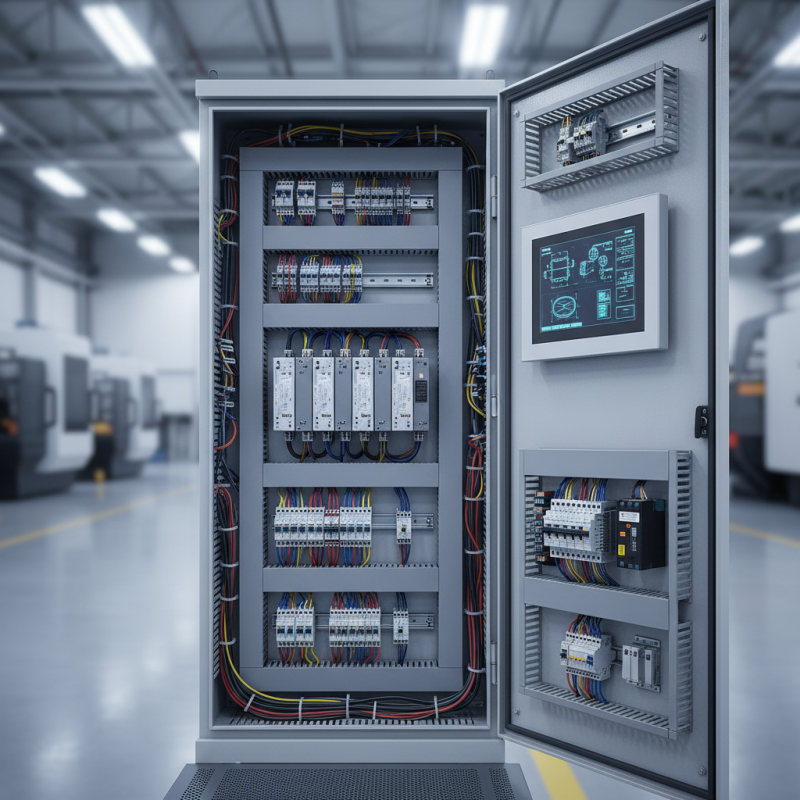

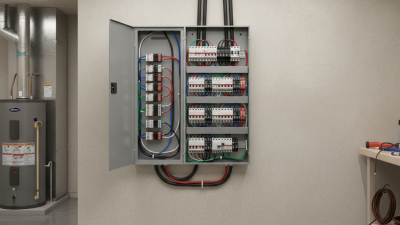
When designing control panels with programmable logic controllers (PLCs), it is essential to focus on efficiency and clarity. A well-organized layout facilitates troubleshooting and maintenance, which can significantly reduce downtime. Start by choosing a suitable enclosure that protects the components while allowing for adequate airflow and easy access. Use clear labeling for inputs, outputs, and power supplies to enhance readability and ensure operators understand the control system quickly. Additionally, consider the placement of PLCs in relation to other components to minimize wiring complexity, which not only simplifies installation but also enhances overall system robustness.
Another critical aspect is to implement standardized wiring practices. Utilizing color-coded wires and uniform terminal blocks creates consistency throughout the control panel, making it easier for technicians to identify connections. Proper grounding techniques help prevent electrical noise, which can interfere with the PLC’s operation and affect performance. Also, integrating built-in diagnostics within the PLC can provide real-time feedback, allowing for proactive monitoring of system health. Overall, emphasizing organization, clarity, and standardization in your PLC control panel design can lead to more reliable and maintainable industrial systems.
When designing a control panel that incorporates Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs), understanding their architecture is paramount for effective integration. A PLC typically consists of several key components, each serving a distinct function that contributes to the overall operation of the control system. The central processing unit (CPU) acts as the brain of the PLC, executing control instructions, processing inputs, and generating outputs based on the programmed logic. It ensures effective data handling and timely execution of tasks, making it critical for real-time operations.
Along with the CPU, input and output modules play essential roles in the PLC architecture. Input modules receive signals from various field devices, such as sensors and switches, converting them into a format that the CPU can process. Conversely, output modules interface with actuators and other control devices, translating the CPU's commands into physical actions within the system. Additionally, communication interfaces enable the PLC to interact with other devices and systems, facilitating data exchange and coordination in complex control environments. Understanding the interconnectivity and functionality of these components allows engineers to design more efficient and reliable control panels tailored to specific industrial applications.
When selecting the appropriate Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) for your control panel design, several critical factors must be considered to ensure optimal performance and reliability in your application. According to a 2022 report by the International Society of Automation, about 47% of industrial automation failures can be attributed to improperly selected or outdated controllers. Therefore, understanding the specific requirements of your application is essential before making a decision.
Firstly, assess the complexity of the tasks your PLC will handle. This includes evaluating the number of I/O points, the types of signals involved (digital vs. analog), and the expected response time. For applications requiring high-speed data processing, a PLC that supports real-time operations is necessary. Moreover, compatibility with other manufacturing equipment and the ease of integration into existing systems should not be overlooked. A McKinsey & Company report emphasizes that integrating new control systems can reduce downtime by up to 25% when proper attention is given to compatibility and system architecture.
Additionally, consider the scalability and future-proofing of your PLC choice. As industries increasingly embrace Industry 4.0, the demand for PLCs capable of handling IoT integration and advanced data analytics is on the rise. A forecast by MarketsandMarkets predicts a compound annual growth rate of 7.3% for the global PLC market from 2021 to 2026. Investing in a scalable PLC that allows for easy upgrades and expansion can ensure the longevity of your control systems and adaptability to evolving technologies.
Effective Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) programming is essential for building reliable and efficient control logic in industrial applications. According to recent industry reports, approximately 70% of automation failures can be traced back to inadequate programming practices. By focusing on best practices, engineers can significantly reduce downtime and improve system performance.
One key aspect of efficient control logic design is the use of structured programming techniques such as modular design and state-based logic. This approach not only enhances readability and maintainability of the code but also streamlines troubleshooting processes. In fact, a study from the Automation of Control Systems Association found that projects employing modular programming techniques reported a 30% decrease in debugging time. Furthermore, utilizing simulation tools during the design phase can help in validating logic before deployment, minimizing costly errors in operational settings.
Another critical factor involves the implementation of standardized naming conventions for inputs and outputs, which boosts clarity and simplifies future modifications. Reports indicate that clear documentation and consistent labeling can improve team collaboration and reduce the time required for onboarding new engineers. By adhering to these practices, organizations can achieve more efficient control logic, ultimately leading to enhanced productivity and reduced project costs over time.
When designing control panels, wiring and connectivity play a critical role in ensuring system reliability and performance. One of the primary considerations in this aspect is the choice of wire types and gauges. Using appropriate wire sizes minimizes resistance and heat generation, which can lead to performance issues over time. Additionally, organizing wires neatly not only enhances aesthetics but also simplifies troubleshooting, making it easier for technicians to manage the system.
Another essential factor is the quality of connections. Employing sturdy connectors and terminals can reduce the risk of intermittent connections that may lead to system failures. Implementing proper strain relief mechanisms prevents wire damage and ensures that connections remain secure under various environmental conditions. Furthermore, documenting the wiring layout with clear diagrams aids in maintenance and future upgrades, fostering a reliable control panel ecosystem that can adapt to evolving operational needs.
In the realm of automation and control systems, effectively implementing PLC in control panel design is essential for achieving optimal performance. The article outlines crucial tips that begin with understanding the PLC architecture, emphasizing the key components and their functions. Selecting the right PLC for specific applications involves considering factors such as input/output requirements and processing capability.
Furthermore, the article highlights best practices for designing efficient control logic, which is fundamental for reliable PLC programming. It also stresses the importance of proper wiring and connectivity to ensure system reliability. Lastly, the methods for testing and validation are discussed, which serve to verify PLC performance within control panels, ensuring they meet operational standards and safety protocols. Overall, these insights provide a comprehensive guide for effective PLC utilization in control panel design.