When it comes to setting up a safe and efficient electrical system in your home, choosing the right Electrical Panel is crucial. According to renowned electrical engineer and industry expert, John Smith, “The electrical panel serves as the heart of your home’s electrical system, managing the flow of electricity and ensuring safety.” This statement highlights the importance of selecting an Electrical Panel that aligns with your specific household needs, as a well-chosen panel can drastically enhance performance while minimizing potential hazards.
In today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape, the demand for reliable power supply continues to grow. Homeowners need to consider various factors such as capacity, configuration, and safety features when making a selection. With options ranging from basic panels to advanced smart systems, understanding your requirements is essential in making an informed decision. As you embark on the journey of choosing an Electrical Panel, remember that investing time in research will ultimately lead to a safer and more efficient home environment.

Understanding the basics of electrical panels is crucial for any homeowner looking to enhance their electrical system's efficiency and safety. An electrical panel, also known as a circuit breaker box, serves as the hub of your home's electrical system, distributing power to various circuits and protecting them from overload. It is designed to manage electricity flow while providing a means to shut off power during emergencies or system maintenance. Familiarizing yourself with the different components, such as breakers, bus bars, and neutral bars, can help in making informed decisions when upgrading or installing your panel.
When selecting an electrical panel, consider these essential tips. First, assess your power needs by evaluating the total wattage of all electrical devices in your home. This will help you determine the appropriate size and amperage of the panel. Later, think about future expansions; it's a good idea to choose a panel with capacity for additional circuits in case you decide to upgrade your electrical system or add new appliances. Lastly, prioritize safety features, such as surge protection and properly rated breakers, to ensure reliable operation and to safeguard your home against electrical hazards.
Understanding these fundamentals and adhering to these tips can simplify the process of selecting the right electrical panel, ensuring your home's electrical system is robust and efficient.
When selecting the right electrical panel for your home, the first step is to assess your household's power needs. Understanding your typical energy consumption and potential future needs is crucial. Start by reviewing the appliances and devices you regularly use. Calculate the total wattage to get a clear picture of your current power demand. Additionally, consider any future upgrades or expansions, such as adding new appliances, a home office, or an electric vehicle charger.
Tip 1: Conduct a comprehensive audit of your home’s electrical usage. List all major appliances, their wattage, and how often they’re used. This will help you gauge the minimum capacity required for your electrical panel.
Tip 2: Factor in safety margins. It’s wise to choose a panel that can handle at least 20% more than your calculated needs. This buffer allows for any unexpected power surges and accommodates future enhancements without the hassle of immediate upgrades.
Tip 3: Consult with a licensed electrician to ensure your assessments are accurate. They can provide valuable insights into local codes and may offer suggestions based on their experience with similar homes. Their expertise will ensure that your electrical panel not only meets your current requirements but is also future-ready.
When choosing a residential electrical panel, several key features should guide your decision. First and foremost, the panel's amperage rating is crucial, as it determines the amount of electrical load the system can handle. Most modern homes require a panel rated for at least 200 amps, which supports contemporary high-demand electrical appliances and systems. Evaluating the amperage ensures that your home can safely and efficiently manage its power needs without the risk of overload or electrical failures.
Another important aspect is the panel's configuration and the number of circuit breakers it can accommodate. A panel should offer enough slots for current and future circuits, reflecting your home's growth and any potential renovations. Additionally, consider the type of breakers included; modern panels might feature both standard and GFCI (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter) breakers for enhanced safety, especially in moisture-prone areas like kitchens and bathrooms. Lastly, assess the panel's overall build quality and compliance with local codes, as these factors contribute significantly to electrical safety and longevity.
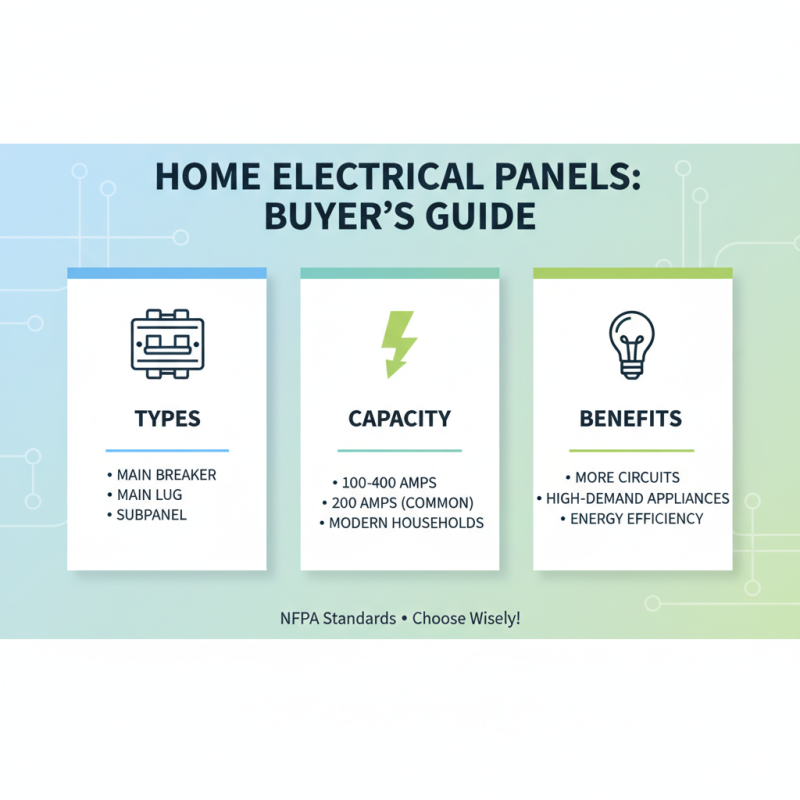
When evaluating different types of electrical panels for your home, understanding the features and specifications is crucial. There are several panel types available, including main breaker panels, main lug panels, and subpanels. According to the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), standard residential electrical panels typically range from 100 to 400 amps, with the most common being the 200-amp panel, which is often sufficient for modern households. A 200-amp panel supports a larger number of circuits and can accommodate high-demand appliances, ultimately enhancing your home’s energy efficiency.
Another important aspect to consider is the type of circuit breakers used in these panels. The choice between standard circuit breakers and modern smart breakers can significantly impact the safety and manageability of your home’s electrical system. Research by the Electrical Safety Foundation International (ESFI) indicates that smart circuit breakers, which can monitor energy usage in real-time, help homeowners make informed choices about their energy consumption, enabling potential savings of up to 20% on electricity bills. Furthermore, these breakers enhance safety by providing alerts for unusual fluctuations or potential faults, adding an extra layer of protection to your home.
When selecting an electrical panel, evaluating your home’s power requirements and the available panel types will empower you to make an informed choice. With safety standards set by organizations such as the National Electrical Code (NEC), ensuring your panel meets these guidelines is essential to safeguard against electrical hazards. Investing in the right panel can not only enhance your home’s electrical capacity but also contribute to long-term energy efficiency and safety.
When selecting the right electrical panel for your home, it is crucial to avoid some common mistakes that can lead to costly issues down the line. One prevalent misstep is underestimating the electrical load requirements. According to a report from the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), improperly sized electrical panels can lead to overheating and potential fire hazards. Homeowners should assess their current and future power needs by considering all appliances, devices, and possible expansions. A professional assessment may recommend a panel with a capacity that exceeds current demands, often suggesting a minimum of 200 amperes for modern homes.
Another mistake is neglecting to consider the type of panel that suits the home’s layout and electrical needs. A study by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) emphasizes that different types of panels, such as main breaker panels and subpanels, offer distinct advantages depending on the number of circuits and distribution requirements. Homeowners should evaluate their existing wiring and future upgrades to ensure compatibility with the chosen panel. Additionally, overlooking the necessity of proper safety features, such as surge protection and circuit breakers, can lead to increased vulnerability to electrical faults and interruptions. By avoiding these mistakes, homeowners can make informed decisions that enhance safety and efficiency in their residential electrical systems.
| Tip/Mistake | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Assess Your Power Needs | Evaluate the total load requirements for your home, including appliances and electronics. | High |
| Choose the Right Amperage | Select a panel with sufficient amperage to handle your household demand. | High |
| Consider Future Expansion | Plan for potential electrical upgrades or additions to your home. | Medium |
| Avoid Underestimating the Size | Choosing a panel that is too small can lead to overloads and safety risks. | High |
| Neglecting Code Compliance | Ensure that the panel meets local electrical codes and regulations. | Very High |
| Research Panel Types | Understand differences between sub-panels, main panels, and panel boards. | Medium |
| Ignoring Professional Help | Consulting with a licensed electrician can prevent costly mistakes. | Very High |