In the world of industrial measurement, accuracy is critical. The development of innovative Measuring Tanks is a game changer. These tanks play a vital role in many sectors, including manufacturing and agriculture. They ensure precise measurement of liquids, enhancing productivity.
Recent advancements have introduced smart technologies in Measuring Tanks. These innovations include advanced sensors and automated systems. Such features allow for real-time monitoring and data collection. However, implementing these technologies can be challenging. Training staff is essential to maximize efficiency and minimize errors.
There are still deficiencies in current designs. Some tanks don't handle extreme conditions well. This can lead to inaccurate readings. Furthermore, maintenance can be overlooked, impacting reliability. As we explore the 2026 innovations, it's clear there's room for improvement in the quest for precision in Measuring Tanks.

In 2026, measuring tank designs are set to undergo remarkable changes. These innovations aim to enhance measurement accuracy significantly. One noteworthy design is the integration of smart sensors. These sensors can detect minute changes in liquid levels. They provide real-time data, allowing operators to make informed decisions.
Another exciting development is the use of advanced materials. Lightweight composites can reduce tank installation challenges. They also improve durability under harsh conditions. However, the cost-benefit analysis of these materials remains a concern. Many are still unsure if the investment justifies the potential for greater accuracy.
Visual indicators are also being rethought. Traditional gauges often lead to misinterpretation. New designs incorporate clearer readouts and color-coded levels. While they promise better visibility, some may still struggle to understand the changes. The progress in measuring tank design is promising, but critical reflections on usability and cost-effectiveness are essential.
The impact of smart sensors on measurement precision in tanks is profound. These sensors enhance accuracy by providing real-time data. A recent industry report indicates that smart sensor technology can reduce measurement errors by up to 30%. This has significant implications for industries like oil and gas, warehousing, and chemical processing.
Smart sensors utilize advanced algorithms to interpret data from various sources. They can detect minor changes in tank levels that traditional methods might miss. However, implementing these technologies may be challenging. Not all facilities are equipped to handle the data generated. Companies need to invest in proper systems and training.
Tips: Regularly calibrate smart sensors to maintain accuracy. Integrate software that can analyze sensor data effectively. Consider the environmental conditions, as they can impact sensor performance. Be mindful that over-reliance on technology may lead to overlooking manual checks. Balancing both methods often yields the best results.
| Innovation | Sensor Type | Measurement Range | Accuracy (% Full Scale) | Communication Protocol | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Laser Level Measurement | Laser Sensor | 0-20 m | ±0.1% | RS485 | Water Tanks |
| Ultrasonic Level Transmitter | Ultrasonic Sensor | 0-10 m | ±0.3% | Modbus | Wastewater Treatment |
| Radar Level Gauge | Microwave Radar | 0-30 m | ±0.5% | WLAN | Chemical Storage |
| Capacitance Level Sensor | Capacitive Sensor | 0-5 m | ±0.2% | I2C | Food and Beverage |
| Smart Pressure Sensors | Pressure Sensor | 0-100 mH2O | ±0.1% | Ethernet | Oil and Gas |
The integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) into measuring tanks has revolutionized data monitoring. Real-time updates allow operators instant access to critical metrics. Sensors gather information continuously, providing data on liquid levels, temperature, and pressure. This connectivity helps in making prompt decisions, reducing delays.
However, this technology isn't flawless. Connectivity issues can disrupt data flow. Users must be prepared for potential outages. Regular maintenance of sensors is crucial. A smart tank is only as reliable as its components. Moreover, filtering through abundant data can be overwhelming. Operators may struggle to identify what’s significant.
Despite its challenges, IoT in measuring tanks improves efficiency significantly. Data-driven insights can lead to better resource management. Analytics can highlight trends over time. This promotes proactive measures instead of reactive ones. Continuous improvement is necessary as technology evolves. Each advancement brings new hurdles and opportunities. The goal is not perfection but progress.

In recent years, advancements in materials science have significantly impacted the durability of measuring tanks. Traditional materials often suffer from corrosion and wear, reducing their lifespan and accuracy. A study from the International Journal of Industrial Technology reveals that over 25% of measuring tank failures are due to material degradation. This highlights the need for innovative solutions in the industry.
The introduction of composite materials offers promising results. These materials can withstand extreme conditions while providing greater resistance to chemical damage. For example, epoxy resins and fiberglass composites have emerged as popular choices among engineers. They are not only lightweight but also possess enhanced strength. Yet, the initial cost remains a concern, potentially deterring widespread adoption.
Furthermore, sustainability plays a crucial role in material selection. Biodegradable options are being explored, but they often lack robustness. Balancing eco-friendliness and durability is a challenge. The industry must reflect on this as it moves forward. Current trends indicate that up to 30% of manufacturers prioritize eco-friendly materials, but performance cannot be compromised. Data suggests that a strategic approach is essential to integrate both innovations and practical applications effectively.
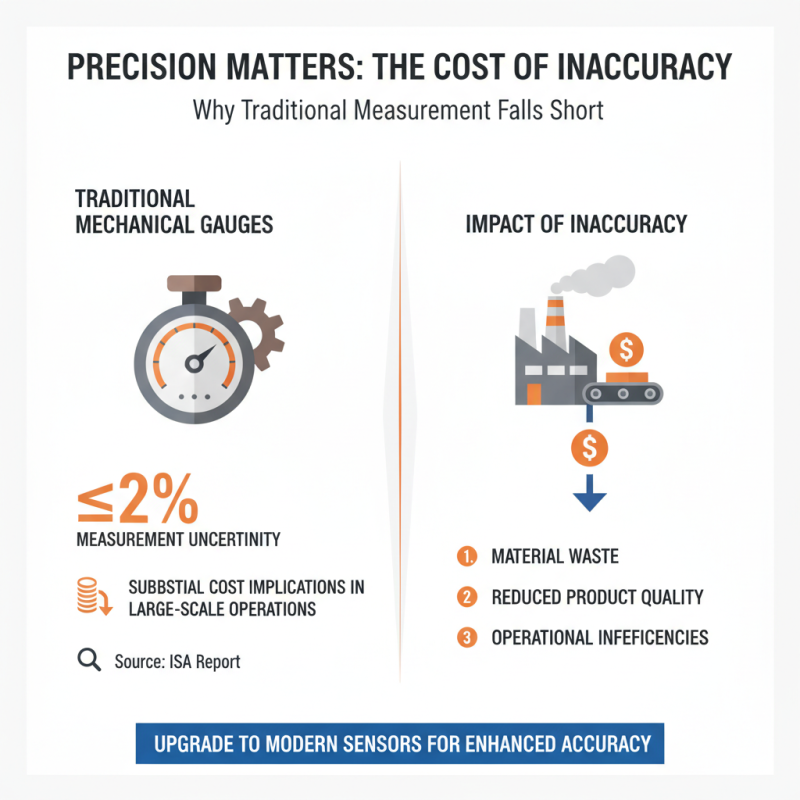
Accurate measurements in industries are critical. Traditional measurement technologies, often based on mechanical systems, can introduce errors. For instance, a report by the International Society of Automation found that mechanical gauges can have a measurement uncertainty of up to 2%. This margin may seem small, but in large-scale operations, it results in substantial cost implications.
Modern measurement technologies have emerged to counter these issues. Digital measurement systems often boast an accuracy of ±0.5%, significantly enhancing precision. They provide real-time data and minimize human intervention. However, they are not without challenges. Initial setup costs can be high, which may deter some businesses. Additionally, the learning curve is steep for staff unfamiliar with newer systems.
Comparatively, some sectors still rely on traditional methods. The familiarity aspect can enhance function reliability, but outdated practices may not meet escalating standards. A balance is essential. Embracing innovations is vital, yet numerous firms hesitate to let go of the tried and true. Continuous reflection on what's effective versus what's outdated could lead to better operational efficiency.