In the world of industrial automation, understanding "Plc In Control Panel" is essential for beginners. James Anderson, an expert in automation systems, once said, "The control panel is the heart of any automation system." This highlights the crucial role that PLCs play in controlling machinery and processes.
PLC, or Programmable Logic Controller, is a pivotal technology in control panels. It allows users to automate various tasks efficiently. Beginners often find PLCs complex, yet their importance cannot be overstated. The control panel remains a central hub for all operations, where PLCs make decisions based on sensor inputs.
Learning about "Plc In Control Panel" opens doors to a career in automation. As one delves into this topic, it’s easy to feel overwhelmed. However, with practice, even the most intricate systems become manageable. Understanding the mechanics behind PLCs can lead to innovative solutions in industries that rely on automation.

A PLC, or Programmable Logic Controller, plays a crucial role in modern control panels. It acts as the brain, processing inputs and controlling outputs. A PLC is designed to be robust and reliable in challenging industrial environments. According to a recent industry report, 75% of automation applications utilize PLCs for their flexibility and scalability.
The primary function of a PLC is to automate tasks. It takes various inputs from sensors and switches, processes the data, and sends commands to actuators or motors. This seamless integration enhances efficiency and safety in operations. Interestingly, about 80% of manufacturers report improved productivity after implementing PLC systems. However, the complexity of programming can be a barrier for some users.
Moreover, PLCs are essential in data collection. They can gather operational data in real time. Many industries benefit from this, especially in quality control. A noted downside is that misconfiguration can lead to errors in operation, causing unexpected downtime. Continuous training and updating skills are necessary for effective usage. This reflects the ongoing need for improvement in the PLC landscape.
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) are essential in automation systems. They control machinery by processing data from inputs and controlling outputs. Understanding their core components can help beginners grasp their functionality.
Inputs are crucial. They receive signals from various sensors or switches. For instance, temperature sensors might feed data to the PLC. The input signals can be digital or analog. Digital inputs indicate on/off states, while analog inputs measure varying levels. This can be pressure, speed, or temperature. Each input plays a specific role in system operation.
Outputs drive the actions in a system. When the PLC processes input signals, it sends commands to actuators or relays. These outputs execute tasks such as turning on a motor or activating a valve. The brain of the PLC, the CPU, decides the operations based on predefined logic. It processes different inputs, often leading to unexpected scenarios. Sometimes, the signals don’t match expected patterns. It's in these moments that one must reflect on the logic behind decisions. Managing these components effectively is key. Understanding their interaction can lead to better troubleshooting and system efficiency.
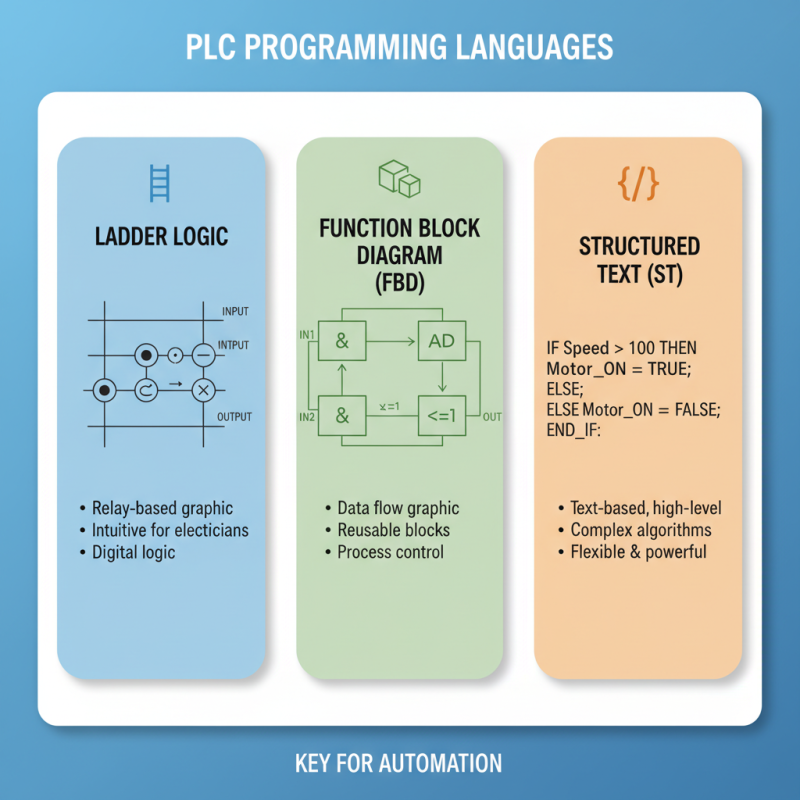
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) are essential in automation tasks. Understanding their programming languages is key for effective use. Common PLC programming languages include Ladder Logic, Function Block Diagram (FBD), and Structured Text. Each has unique features suited to different applications.
Ladder Logic, one of the most popular languages, mimics electrical relay logic. With over 40% of PLC users preferring Ladder Logic, its simplicity is appealing to beginners. It visually represents circuits, making debugging intuitive. However, its limitations can surface in complex operations.
FBD is graphical and allows for more complex functions without extensive text. It uses blocks to represent functions. Data from the International Society of Automation shows that FBD is gaining traction, especially in industries requiring data manipulation and integration. Structured Text resembles traditional programming languages. It’s often less understood by beginners but offers flexibility in complex algorithms.
Each language has its pros and cons. Choosing the right one depends on the specific project needs. Understanding these languages is crucial for aspiring PLC programmers. As automation grows, so does the importance of mastering these programming styles.
Industrial automation heavily relies on Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs). These devices are essential for controlling machinery and processes. They improve efficiency and reduce human errors. PLCs are in many settings—factories, assembly lines, and more. For instance, a car manufacturing plant uses PLCs to monitor robots. These robots weld and assemble parts with precision. Human operators can oversee multiple machines, creating a smoother workflow.
Statistics highlight the impact of PLCs. In industries using automation, productivity can increase by up to 60%. Companies report fewer errors and reduced waste. One case involved a food processing plant. By implementing PLCs, they cut operational costs significantly. The integration streamlined production, decreased downtime, and improved product quality. However, the transition isn’t always easy. Some workers face challenges adapting to new systems. Training is crucial for efficiency.
Understanding the role of PLCs in automation can empower businesses. Learning from these applications can lead to better practices. Emphasizing hands-on experience is vital. Mistakes will happen, but they can lead to growth. Embracing technology is key to thriving in today’s competitive landscape.
This chart illustrates the percentage distribution of various applications of Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) in industrial automation. As shown, manufacturing applications represent the largest share, followed by energy management and process control. This highlights the significance of PLCs in optimizing industrial processes across different sectors.
PLCs, or Programmable Logic Controllers, play a vital role in control systems. They automate processes and enhance efficiency. Companies find that using PLCs reduces operational costs significantly. For example, they can lower labor costs through automation. Tasks that once required manual labor can now be performed by a PLC. This shift leads to faster production rates.
Another advantage is reliability. PLCs are designed for industrial environments. They endure extreme temperatures and vibrations, which helps prevent failures. However, their effectiveness is not guaranteed. Improper programming can lead to unexpected shutdowns. Regular maintenance is crucial to avoid issues. Users must remain vigilant for signs of malfunction.
Cost efficiency and reliability are key benefits of utilizing PLCs in control systems. In today's competitive landscape, businesses cannot overlook these advantages. Embracing PLC technology may require an initial investment, but the returns often justify the cost. Keeping systems updated is essential. Ignoring this can lead to lost opportunities and increased downtime.