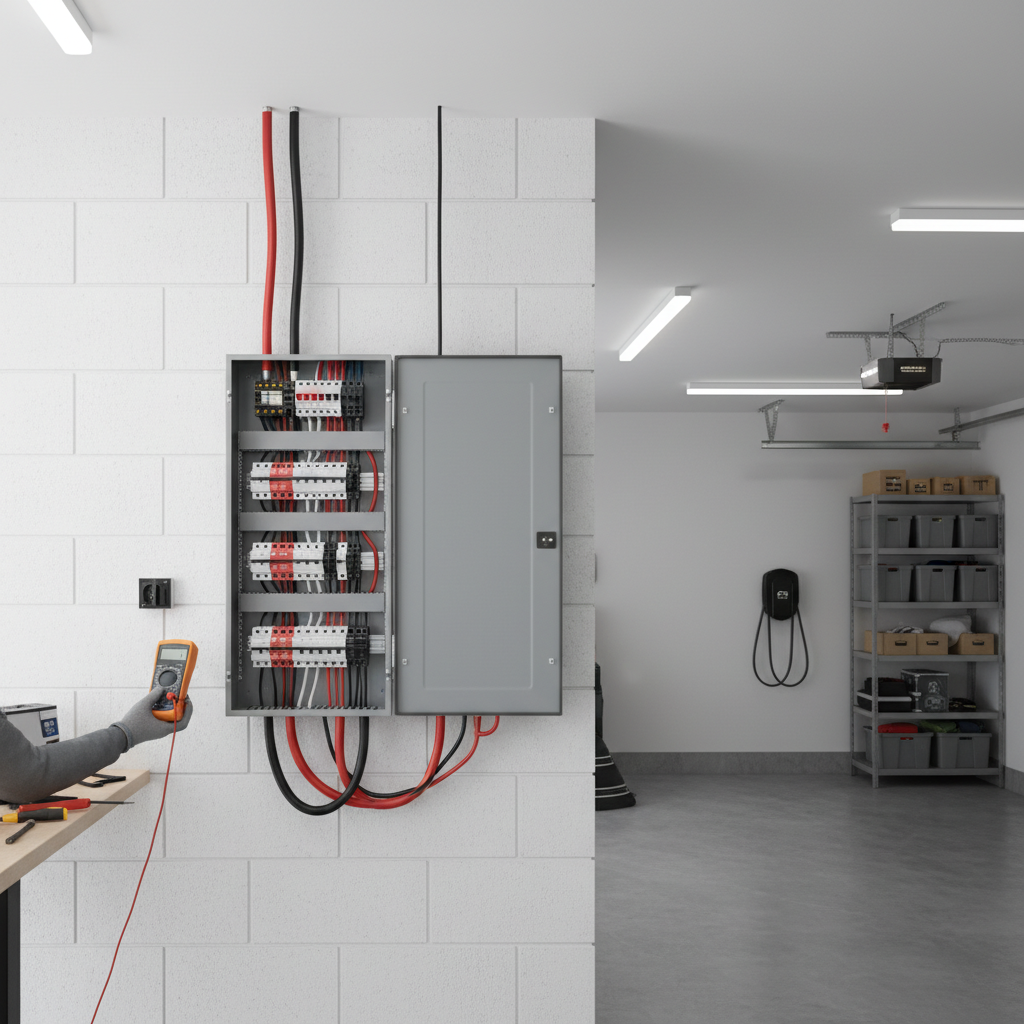
Choosing the right electrical panel for your home is a crucial decision that can impact the safety, efficiency, and functionality of your electrical system. According to the National Fire Protection Association, outdated or improperly installed electrical panels contribute to approximately 51,000 home fires annually in the U.S. This alarming statistic underscores the importance of selecting an appropriate electrical panel that meets the needs of modern households. With advancements in technology and increasing electrical demands due to smart home devices, the selection process has become more nuanced than ever.
Renowned electrical industry expert, John Smith, emphasizes the significance of this choice: "A well-chosen electrical panel not only provides adequate power management but also enhances the overall safety of your home." To assist homeowners in navigating this complex landscape, understanding the essential features, capacity requirements, and compliance with local codes is vital. In this guide, we will explore the ten essential tips for selecting the right electrical panel, empowering you to make informed decisions that ensure the reliability and safety of your home’s electrical system.
When choosing the right electrical panel for your home, understanding your electrical load requirements is paramount. Each electrical device in your home has a specific power demand, and when these demands are summed up, they determine the overall load your panel must support. This load can fluctuate based on lifestyle changes, the addition of new appliances, or renovations. Therefore, a comprehensive evaluation of your current and future power needs is essential to prevent potential overloads and ensure safety.
Assessing your home’s electrical load begins by identifying all the appliances and devices that will be connected to the panel. Consider high-demand items such as air conditioning units, electric heaters, and large kitchen appliances, as they significantly contribute to your load calculations. Once you have a clear picture, consult with an electrician to ensure that your panel not only meets your current needs but also allows for future expansions. Opting for a panel that accommodates a higher amperage than your immediate requirements can provide flexibility and peace of mind as your electrical demands evolve over time.
| Tip Number | Tip Description | Consideration | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Determine your home's electrical load requirements. | Calculate wattage of appliances. | Prevents overloads, ensures efficiency. |
| 2 | Choose the right amperage rating. | Consider future electricity needs. | Allows for growth, avoids replacing panels. |
| 3 | Assess physical space for panel installation. | Measure available wall space. | Ensures proper fit and access. |
| 4 | Consider the panel type (main, sub, etc.). | Know your home's layout. | Optimizes circuit distribution. |
| 5 | Evaluate panel brand reputation. | Research different manufacturers. | Ensures quality and availability of parts. |
| 6 | Select a panel with adequate circuit breaker slots. | Consider current and future circuits. | Provides flexibility for upgrades. |
| 7 | Ensure the panel meets local electrical codes. | Familiarize with local regulations. | Avoids legal issues and fines. |
| 8 | Consider smart panel options. | Research features like remote monitoring. | Enhances energy management. |
| 9 | Check warranty and support options. | Review terms offered by manufacturers. | Provides peace of mind with installation. |
| 10 | Consult with a licensed electrician. | Seek professional guidance. | Ensures safe and effective installation. |
When evaluating circuit breaker ratings for your home, safety and efficiency should be the top priorities. The National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) emphasizes that selecting the appropriate amperage is crucial for protecting your electrical systems and ensuring they can handle increasing power demands, especially in light of the rising prevalence of electric vehicles (EVs). According to a recent report by the International Energy Agency (IEA), the number of electric cars on the road is set to exceed 300 million by 2030, significantly increasing the electricity consumption in households.
With this growing demand, homeowners must consider upgrading their electrical panels to accommodate higher circuit breaker ratings. Circuit breakers are designed to protect your devices and wiring from overloads and short circuits, making it essential to choose models that can reliably manage the current levels required by EV chargers and other high-power appliances. The U.S. Department of Energy projects that residential energy consumption will continue to increase as technological advancements drive the adoption of smart home devices and EVs. Therefore, investing in a modern electrical panel is not just about meeting current needs but also about future-proofing your home against evolving energy demands.
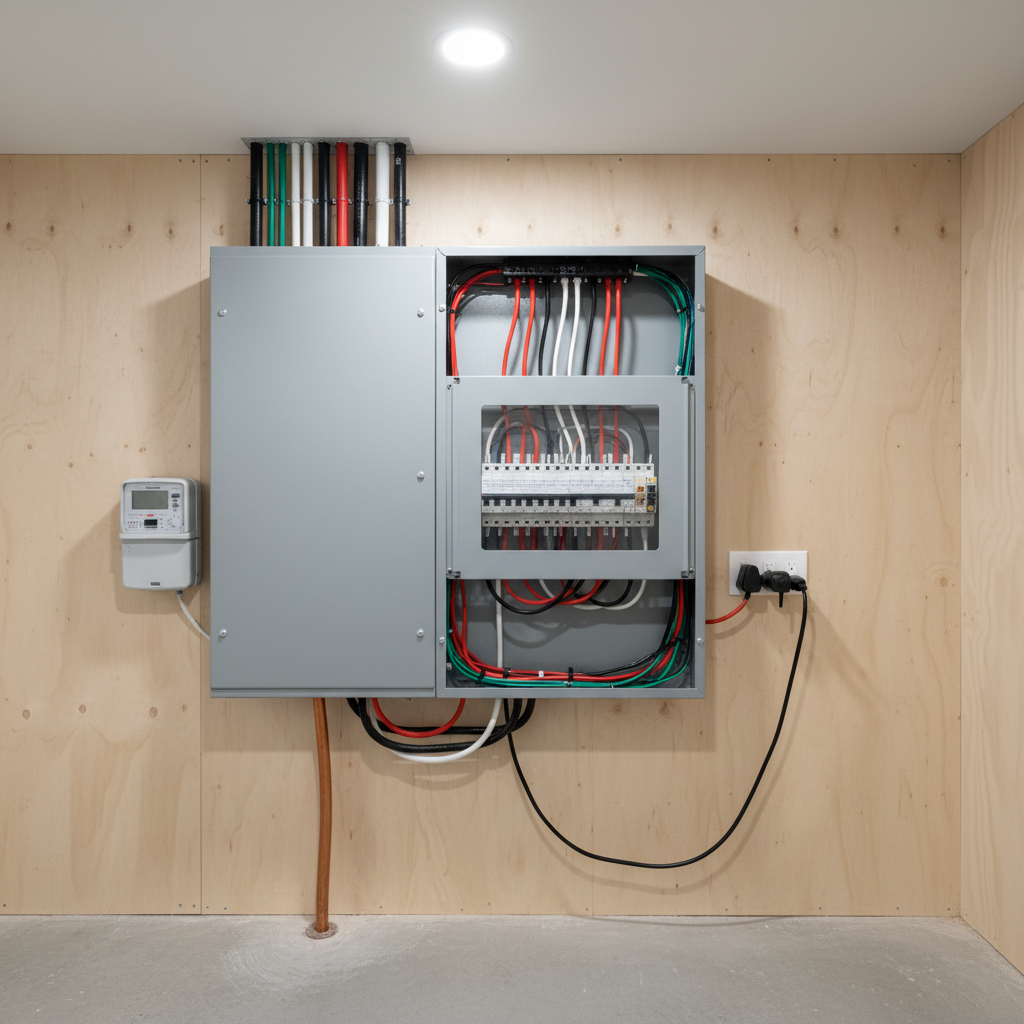

When selecting an electrical panel for your home, one of the most critical decisions revolves around the type of panel: main breaker or main lug. A main breaker panel comes equipped with a built-in circuit breaker that allows you to shut off power to the entire panel, offering a convenient safety feature. This is particularly beneficial during maintenance or emergencies, as it provides immediate control over the electrical system. Additionally, main breaker panels often have a higher capacity for handling electricity, making them suitable for homes with larger power demands.
On the other hand, main lug panels do not have a main breaker and rely on an external disconnect switch. They are typically used in situations where a separate service disconnect is already in place, such as in a subpanel application. While these panels can be more cost-effective upfront, they may require additional safety measures to manage power supply effectively. Understanding the nuances between these two types of panels is essential to ensure that you choose one that fits your specific electrical needs while maintaining safety and compliance with local regulations.
This chart illustrates the popularity distribution between Main Breaker Panels and Main Lug Panels among homeowners. Main Breaker Panels are favored by 70% of homeowners, while Main Lug Panels account for the remaining 30%. Understanding the differences between these panel types can help you make an informed decision when choosing the right electrical panel for your home.
When considering an upgrade to your electrical panel, it is crucial to assess your future expansion needs, particularly concerning capacity. According to the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA), the average modern home requires a minimum of 200 amps to comfortably support contemporary electrical demands. However, with the increasing prevalence of smart home technologies and electric vehicles, many homes may benefit from panels that support up to 400 amps. Planning for this capacity ensures that you have room to grow, avoiding the need for frequent panel replacements.
Moreover, research from the Electrical Safety Foundation International (ESFI) indicates that nearly 70% of homes in the United States were built before 1990 and may not have the electrical capacity needed for today’s lifestyle. This reality suggests that homeowners need to consider not only their current needs but also their potential future requirements. By proactively upgrading to a higher capacity panel, homeowners can accommodate additional appliances, home office equipment, or future electric vehicle charging stations without significant infrastructure changes down the line. This investment not only enhances safety but also adds value to the home by aligning it with contemporary electrical standards.
When selecting an electrical panel for your home, compliance with local electrical codes is paramount. These codes are designed to ensure safety and legality in installations, protecting both your property and its occupants. Familiarizing yourself with the specific regulations in your area can prevent costly mistakes and potential hazards. Always consult a licensed electrician who understands the local codes and can guide you through the installation process.
One essential tip is to ensure that the electrical panel you choose meets the capacity requirements of your home. Calculate your household’s electrical load and select a panel that can accommodate this demand, performing upgrades as necessary. Additionally, consider panels that feature adequate circuit breaker slots to allow for future expansion. This foresight can save you from needing another major installation sooner than expected.
Moreover, prioritize panels equipped with safety features like ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs) and surge protection. These components can help mitigate electrical hazards, in line with local regulations, enhancing overall safety. Remember, adhering to the codes not only fulfills legal obligations but creates a secure environment for your family.







