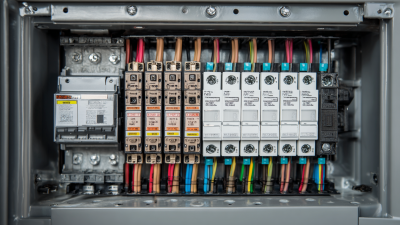
In the realm of modern electrical systems, the role of the panel board is paramount, serving as the nerve center for power distribution and management. According to the Electrical Safety Foundation International (ESFI), panel boards contribute significantly to the overall safety and efficiency of electrical installations, with more than 60% of electrical fires attributed to faulty electrical systems. With the global panel board market projected to reach USD 7.5 billion by 2026, expanding at a CAGR of 4.8%, understanding their functionality and relevance is critical for both residential and commercial applications.
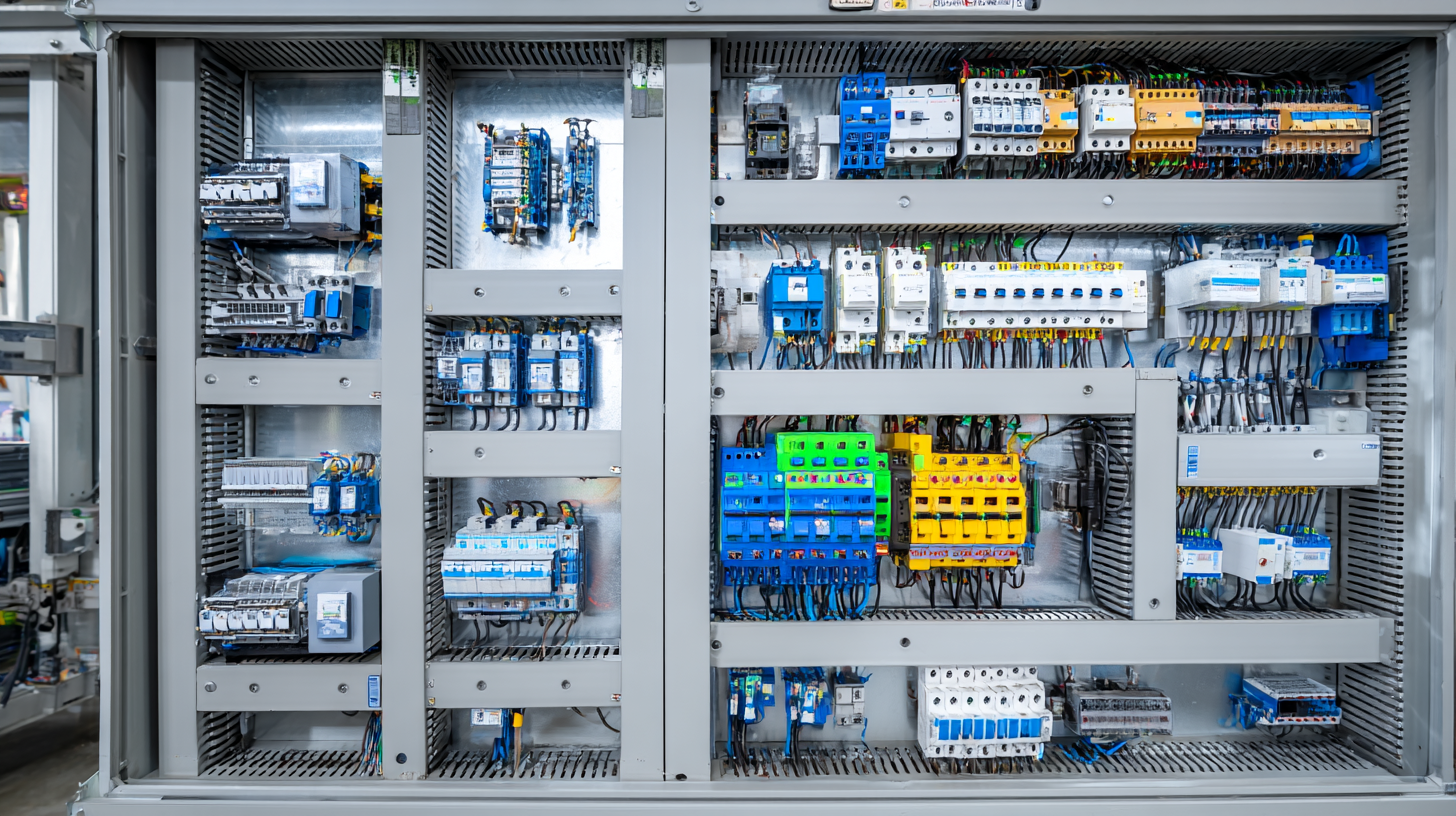
These devices not only facilitate the distribution of electricity but also incorporate advanced technologies for monitoring and protection, ensuring that systems operate within safe limits. Consequently, the essential role of panel boards cannot be overstated, as they are integral to enhancing operational efficiency, ensuring compliance with safety standards, and supporting the growing demand for energy management solutions in an increasingly electrified world.
Panel boards are crucial components in modern electrical distribution systems, serving as the central point where electricity is distributed throughout a facility. They house various circuit breakers and fuses, protecting electrical circuits from overloads and short circuits. By effectively managing the flow of electrical current, panel boards ensure that each appliance and device receives the appropriate voltage and current, optimizing safety and efficiency within the system.
**Tips:** When selecting a panel board, consider the total load demand and ensure the board has adequate capacity for your needs. Regular maintenance checks on the circuit breakers and connections can prevent potential issues such as overheating or failures.
In addition to their protective functions, panel boards also facilitate easier troubleshooting and maintenance. Each circuit is labeled, making it easy for electricians to identify and address issues without disrupting the entire system. This organization not only enhances safety but also minimizes downtime during repairs, allowing for effective management of electrical resources.
**Tips:** Utilize a logbook to track maintenance activities and any issues encountered with the panel board. This practice can help identify recurring problems and assist in future planning for upgrades or replacements.
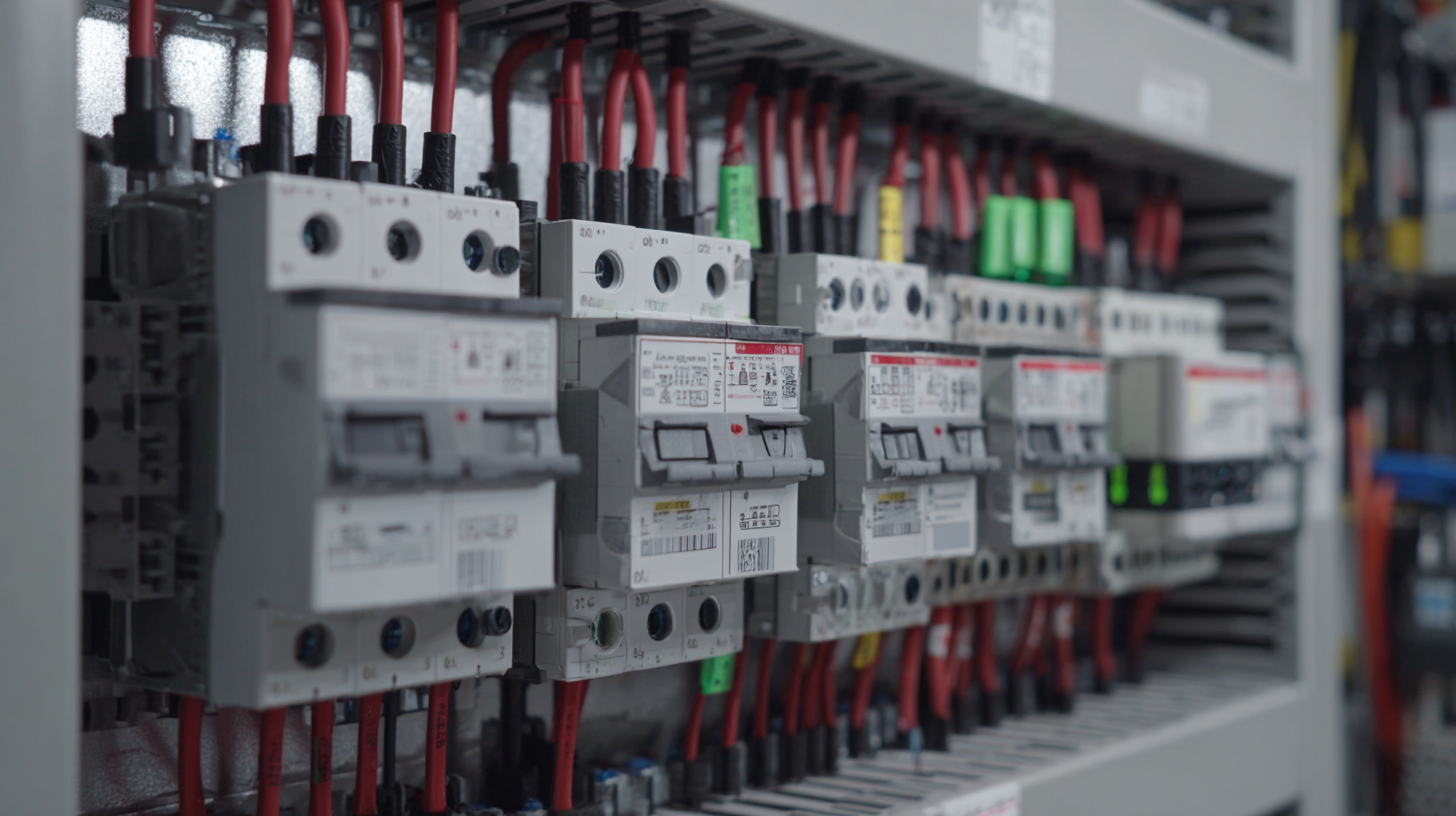

Panel boards play a crucial role in today's electrical systems, serving as the central point for the distribution of electricity throughout residential, commercial, and industrial buildings. Modern panel boards come equipped with several key components that enhance their functionality and safety. These include circuit breakers, fuses, busbars, and a variety of monitoring devices that provide real-time insights into the system's performance. As electrical systems become more complex with the integration of renewable energy sources and smart technologies, the reliability and efficiency of panel boards become even more critical.
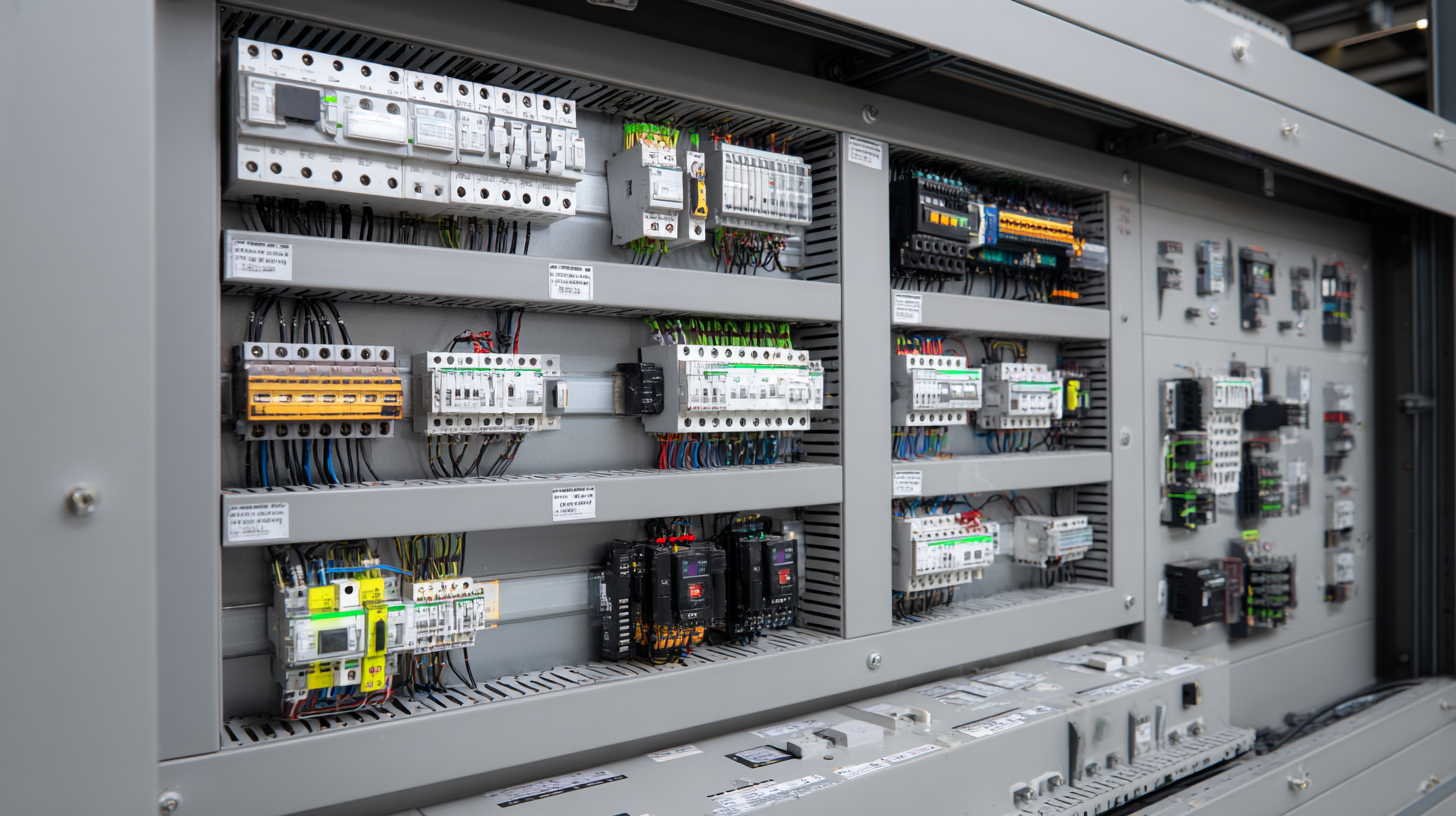

The global market for lightweight automotive body panels is projected to experience significant growth, expanding from $196.24 billion in 2024 to $310.39 billion by 2032, at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.9%. This increase is driven by the automotive industry's shift towards more energy-efficient and fuel-efficient vehicles, necessitating innovative panel board designs that can manage higher electrical loads while minimizing weight. As manufacturers adopt advanced materials and technologies, modern panel boards must evolve to support the increased demand for power distribution and management, ensuring they remain integral components of modern electrical systems.
When working with panel boards, safety should always be the top priority. These essential components of electrical systems can pose various risks if not handled properly. Always ensure that the power is shut off before performing any maintenance or modifications. This not only protects you from electric shock but also prevents potential short circuits that can cause further damage to the electrical system.
**Tips for Safe Panel Board Management:**
1. Use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as insulated gloves and safety goggles to safeguard against accidental contact with live components.
2. Familiarize yourself with the layout of the panel board to understand the locations of circuit breakers and labels, making it easier to respond quickly in an emergency.
3. Regularly inspect the panel board for signs of wear, corrosion, or overheating, addressing any issues immediately to maintain an optimal level of safety.
In addition to preventive measures, proper training is essential when working with panel boards. Always consult the manufacturer’s guidelines and ensure you have the necessary knowledge and skills before interacting with any electrical systems. This will not only enhance your safety but also improve the reliability of the overall electrical infrastructure in your environment.
Proper maintenance of electrical panel boards is crucial for ensuring the safety and efficiency of modern electrical systems. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, poorly maintained electrical panels can lead to up to 30% energy loss, which not only increases operational costs but also diminishes system performance. Regular inspections can help identify signs of wear and tear, potentially preventing hazardous situations such as electrical fires due to overheating or short circuits.
To ensure optimal performance, it is recommended to conduct routine inspections every six months. During these inspections, technicians should check for signs of corrosion, loose connections, or overheating components. Findings from the National Fire Protection Association emphasize that around 50% of electrical fires are attributed to faulty panel boards, reinforcing the need for diligent maintenance. Additionally, keeping the panels clean and free from dust can significantly reduce the risk of electrical failures. Implementing these tips can enhance the longevity and reliability of your electrical systems, contributing to a safer and more efficient working environment.
| Aspect | Description | Recommended Maintenance Frequency | Common Issues |
|---|---|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | Check for any signs of damage, overheating, or corrosion. | Monthly | Visible wear and tear, discoloration. |
| Tightness of Connections | Ensure all connections are tight to prevent arcing. | Quarterly | Loose connections can lead to failures. |
| Cleaning | Remove dust and debris from the panel. | Semi-annually | Overheating due to obstructed airflow. |
| Testing Circuit Breakers | Test the functioning of circuit breakers to ensure proper operation. | Annually | Circuit breakers not tripping as expected. |
| Thermal Imaging | Use thermal imaging to detect hot spots. | Annually | Potential hot spots indicating future failure. |
Emerging technologies have significantly enhanced the performance of panel boards, making them more efficient and adaptable to the demands of modern electrical systems. One of the most impactful developments is the integration of smart technology, which allows for real-time monitoring and management of electrical loads. Smart panel boards can communicate with other devices, providing insights into energy consumption patterns and enabling predictive maintenance. This connectivity not only improves system reliability but also facilitates energy savings, ultimately reducing operational costs.
Another noteworthy advancement is the use of advanced materials and design techniques. Innovations such as modular designs allow for easy scalability and customization, fitting various applications from residential to industrial environments. Additionally, the incorporation of enhanced insulation and thermal management features helps in minimizing energy loss and optimizing the overall performance of the electrical system. These emerging technologies not only bolster the functionality of panel boards but also align with the growing emphasis on sustainability and energy efficiency in modern infrastructure.