Understanding an Electrical Panel is essential for homeowners and electricians alike. According to Jane Smith, a leading expert in electrical systems, “An Electrical Panel is the heart of a home’s electrical system.” This panel directs electricity from the outside into your home and distributes it throughout. Proper knowledge of how it operates can prevent safety hazards.
Electrical Panels contain circuit breakers or fuses that protect your home from overload. In many households, the panel may remain overlooked until an issue arises. This neglect can lead to significant risks, including electrical fires or equipment damage. Each breaker must be appropriately sized for the circuits they serve.
Exploring the functionalities of an Electrical Panel reveals both complexity and simplicity. It requires periodic inspection, yet many people forget to check it. When was the last time your panel received attention? Regular maintenance is crucial, but many find it challenging to prioritize. Understanding its function can help ensure a safer living environment.
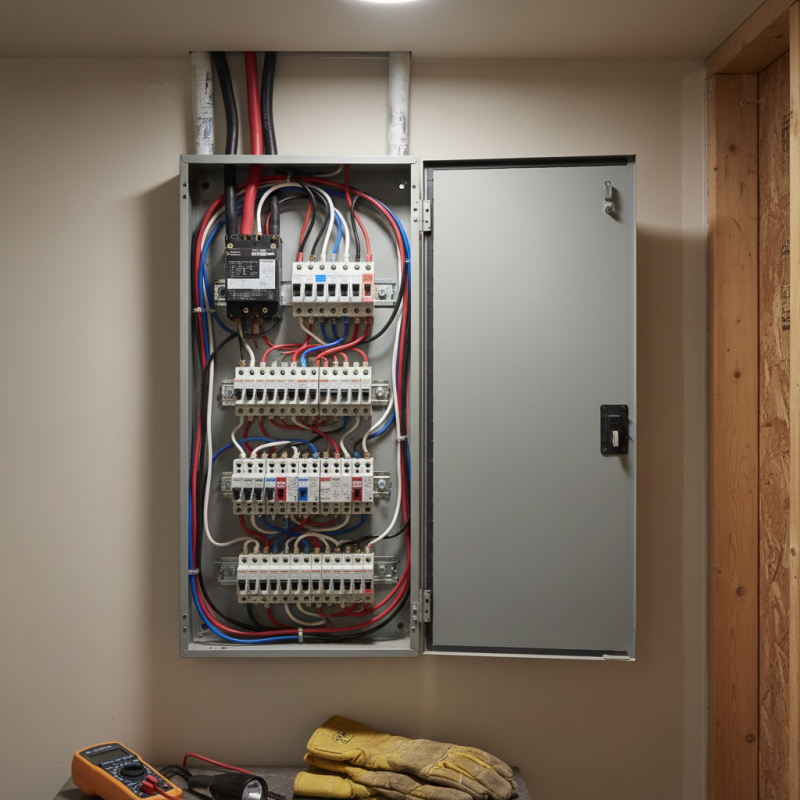

An electrical panel is a vital component in every building. It acts as the main hub, distributing electricity throughout the property. Understanding its function helps ensure safety and efficiency. According to the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), faulty electrical panels can lead to over 60% of household fires.
An electrical panel is crucial for managing the distribution of electricity in a building. It contains several components that work together to ensure safety and efficiency. One key component is the circuit breaker. This device protects against overloads by cutting power when necessary. They can trip unexpectedly, causing frustration. It’s essential to regularly check these breakers to ensure they function properly.
Another important part is the bus bar. This metal strip distributes electrical current to various circuits. A corroded bus bar can lead to problems. It may not effectively carry the required load. Electrical panels also include grounding connections. These ensure that excess electricity safely returns to the ground. If ground connections are loose, it can pose serious risks.
Wiring is another critical component. Properly labeled wires help in identifying circuits. Mislabeling can lead to confusion and potential hazards during repairs. Each component has a role in the overall system. Regular inspection and maintenance of the panel can prevent serious issues. However, many people neglect this step. Understanding these components helps users appreciate the panel’s function. Awareness of potential flaws can lead to better safety practices.
Electricity flows through an electrical panel in a systematic way. The panel acts as a hub for distributing electrical power throughout a building. When electricity comes into the panel, it travels through main power lines. These lines carry high voltages, ready to be split into smaller, manageable currents.
Inside the panel, circuit breakers serve an essential role. They protect the wiring and devices in your home. When too much current flows, breakers will trip, stopping the electricity flow. This safety feature prevents potential hazards. However, sometimes breakers can trip too often, indicating underlying issues.
Wiring connections within the panel can also be a point of concern. Loose connections may generate heat, leading to fires. Regular inspections can help identify these risks. It's crucial to address any signs of wear or damage in the panel. Neglecting these details can result in serious consequences, making awareness essential for safety.
This bar chart illustrates the current distribution across different circuits in an electrical panel. Each circuit serves a specific area of the electrical system, showcasing how electricity flows. The current values are expressed in amperes (A).
Electrical panels come in various types to suit different needs. The most common type is the main service panel. This panel connects directly to the utility line. It distributes electricity throughout the building, powering lights, outlets, and appliances. A subpanel is another type. It's used in larger homes or buildings. Subpanels can relieve the main panel’s load and provide power to specific areas.
Then we have transfer switches. These panels are crucial for backup generators. They allow seamless switching between the grid and generator power. A load center is similar to a main service panel but designed for smaller applications. It simplifies distribution, focusing on efficiency and safety. Each type serves a specific role, dampening potential overload risks in electrical systems.
Choosing the right panel isn’t straightforward. Consider your building's size, electrical load, and future growth. Keep in mind that what works today may not suffice tomorrow. There may be problems if you ignore future expansions. Evaluate your options carefully. Understanding the differences can help prevent costly mistakes later on.
| Panel Type | Description | Typical Applications | Voltage Rating |
|---|---|---|---|
| Main Breaker Panel | Central unit for electrical distribution in residential buildings. | Homes, small businesses. | 120/240V |
| Subpanel | Secondary panel that supports the load of a specific area. | Garages, workshops, additions to homes. | 120/240V |
| Load Center | Panel that controls multiple circuits with circuit breakers. | Residential, commercial electrical systems. | 120/240V |
| Transfer Switch | Allows switching between main power and backup generators. | Emergency power supply, off-grid systems. | 120/240V or higher |
| Smart Panel | Advanced panel with monitoring capabilities and remote access. | Modern homes, energy management. | 120/240V |

Electrical panels play a crucial role in managing power distribution in homes and businesses. However, working with these panels comes with significant safety considerations. Always turn off the main power before beginning any work. This simple step can prevent serious accidents. Use insulated tools to protect yourself from electric shocks.
Before you start, ensure you understand the panel layout. Inspect for any signs of damage, such as rust or corrosion. These could indicate potential hazards. It’s essential to keep the area around the panel clean and free from clutter. This reduces the risk of tripping or accidental contact.
Wearing appropriate personal protective equipment is vital. Safety goggles and gloves can safeguard against sparks and debris. Consider working with a partner, especially for larger jobs. Two sets of eyes can spot potential dangers. Take breaks to assess your progress. Ignoring fatigue can lead to poor decisions. Reflect on your methods and learn from any mistakes made. Safety is paramount when handling electrical panels.